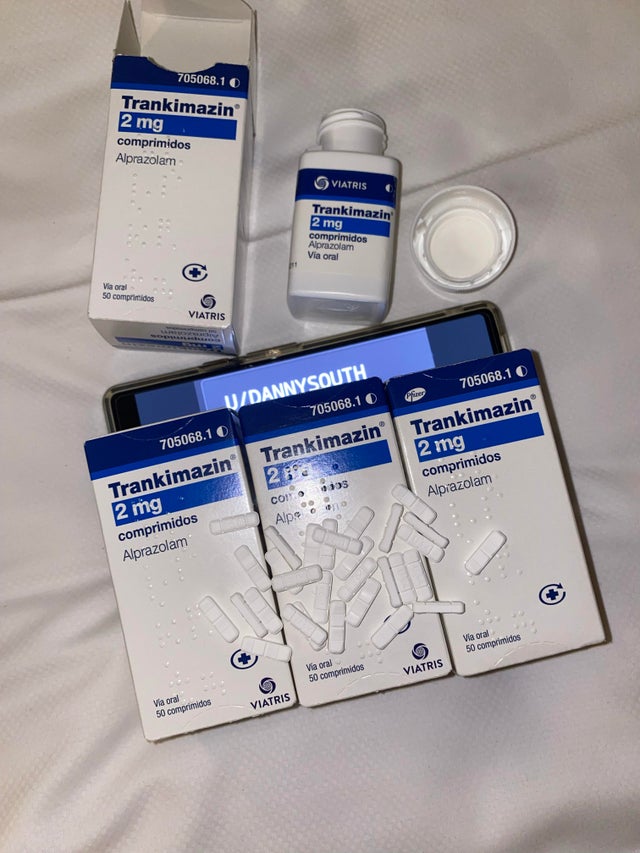
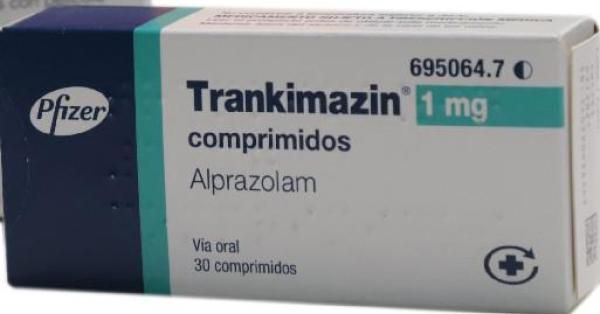
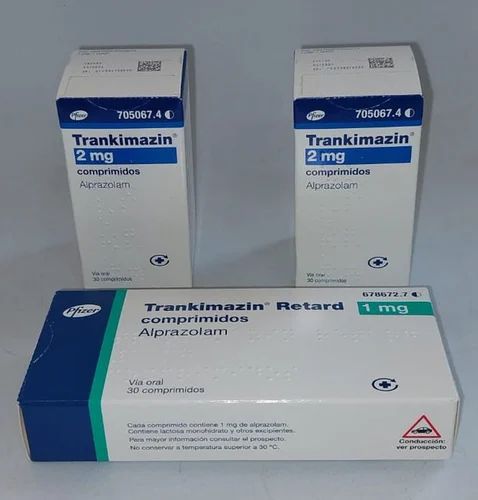
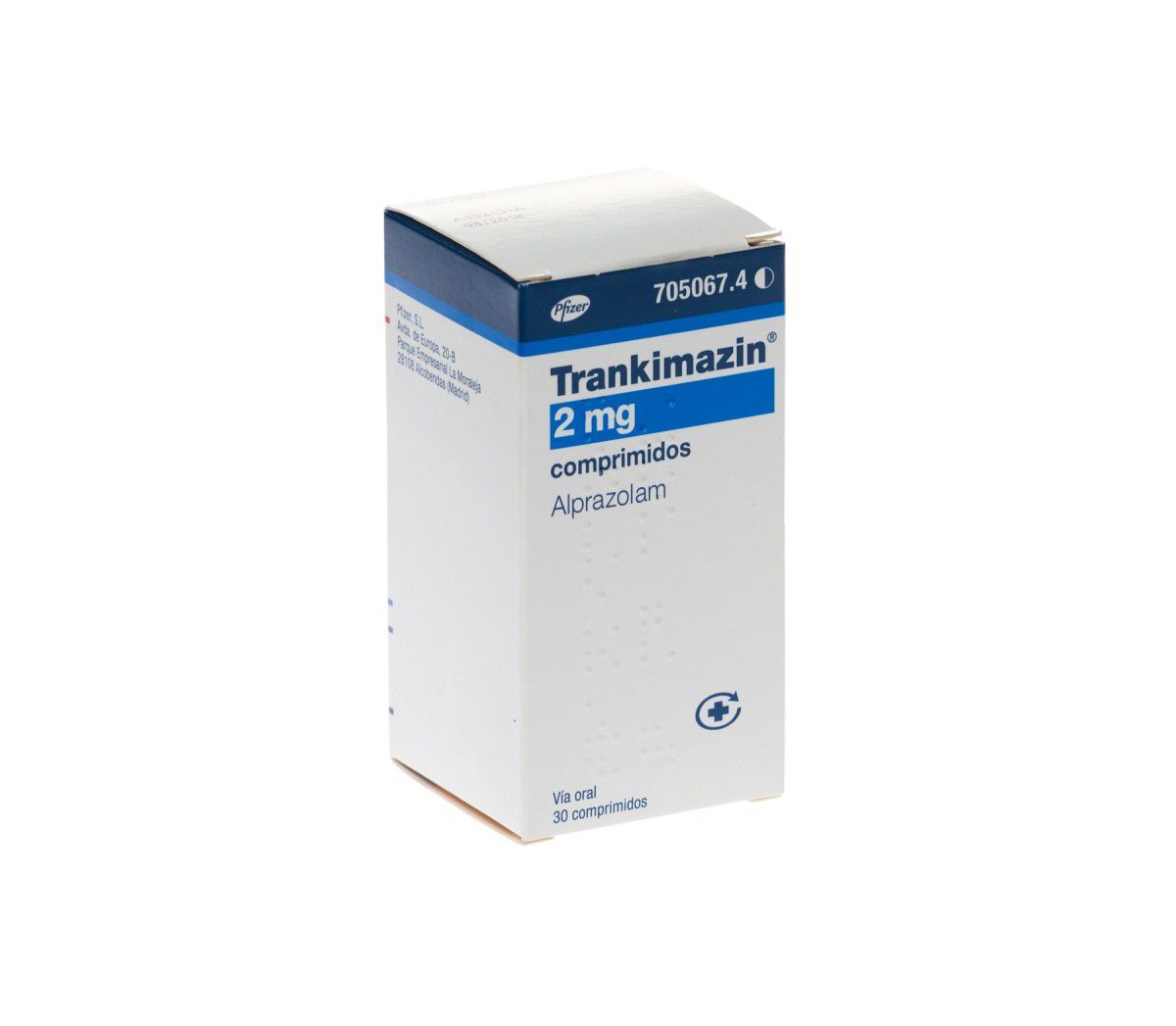
trankimazina 1mg
$60.00 – $600.00Price range: $60.00 through $600.00
BUY QUALITY TRANKIMAZINE 1 MG ONLINE
We are the first online store established in all of Scandinavia.
We sell high-quality medicines that have already been tested by our doctors.
We also sell at a very high price and very fast delivery.
buy your medications with us at mejorfarmaciaonline.com
We sell pain relievers such as: morphine, oxynorm, oxycontin, vicodin, fentanyl, tramadol, dilaudid
We also sell diabetes medications such as: Lantus, Humalog, Levemir, Humulin
then finally, anti-cancer drugs such as; Avastin, Rituxan, Imbruvica
you order with us and receive your medications via dhl
delivered as soon as possible
1. What Trankimazin is and what it is used for
Trankimazin contains the active substance alprazolam. It belongs to a group of medicines called benzodiazepines (anxiolytic medicines).
Trankimazin is used in adults to treat anxiety symptoms that are severe, disabling, or cause great distress to the patient. This medication is for short-term use only.
2. What you need to know before you start taking Trankimazin
Do not take Trankimazin
if you are allergic to alprazolam, benzodiazepines or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
if you suffer from breathing difficulties related or not to sleep (sleep apnea)
if you have a condition called myasthenia gravis which is characterized by muscle weakness
if you have serious liver problems
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Trankimazin.
– If you have any lung, kidney or liver problems.
– If you have felt or are feeling so depressed that you have had suicidal thoughts or ideas.
After continued use of alprazolam, some loss of efficacy (tolerance) may be detected.
There is a risk of developing addiction/dependence when using Trankimazin.
If during treatment you notice symptoms of mania (state of overexcitement, feeling of euphoria or hyperirritability) or hypomania (state of exaggerated excitement and activity).
Treatment with benzodiazepines, including alprazolam, can cause dependence, especially after taking the medication continuously for a long time.
To minimize the risk of dependency, these precautions should be taken into account:
Benzodiazepines should only be taken under medical prescription (never because they have given results in other patients) and they will never be advised to other people.
Do not in any way increase the doses prescribed by the doctor, nor prolong the treatment longer than recommended.
Consult your doctor regularly to decide if you should continue treatment.
Do not combine multiple benzodiazepines regardless of their indication.
When treatment with alprazolam is stopped, symptoms similar to those that led you to start treatment with Trankimazin may appear (rebound effect). To avoid this, it is recommended not to stop treatment abruptly, but to reduce the dose gradually, according to the doctor’s instructions (see section “If you stop treatment with Trankimazin”).
Using alprazolam together with opioid-type medications can cause profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death.
Benzodiazepines may cause memory loss and reactions such as: restlessness, agitation, irritability, aggression, delusions, angry outbursts, nightmares, hallucinations, psychosis, inappropriate behavior, and other adverse behavioral effects. If this occurs, you should stop treatment and consult your doctor.
It is very important that you tell your doctor if you have a history of drug and alcohol use.
Taking Trankimazin with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
Alprazolam may interact with other medications. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any of the following medicines:
Central nervous system depressants, as they can enhance the sedative effect of Trankimazin:
Major tranquilizers (antipsychotics).
Sleep inducers (hypnotics).
Drugs used to treat depression.
Medicines for the treatment of epilepsy (antiepileptics).
Narcotic analgesics and opioids (morphine derivatives), because they can increase the feeling of euphoria, which can lead to an increase in psychological dependence.
Medications used to treat anxiety (anxiolytics/sedatives).
anesthetics
Antihistamines (allergy medications) sedatives.
Concomitant use of Trankimazin and opioids (strong pain relievers, substitution therapy medications (treatment of opioid addiction), and some cough medications) increases the risk of drowsiness, difficulty breathing (respiratory depression), coma, and may be potentially fatal. Because of this, concomitant use should only be considered when other treatment options are not possible.
However, if your doctor prescribes Trankimazin together with opioids, your doctor should limit the dose and duration of concomitant treatment.
Tell your doctor about all opioid medications you are taking and closely follow your doctor’s dosing recommendations. It may be helpful to tell your friends or family so they are aware of the signs and symptoms mentioned above. Contact your doctor if you experience any of these symptoms.
| tablets | 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 210, 240, 270, 300 |
|---|
Be the first to review “trankimazina 1mg” Cancel reply
Related products
ANXIETY
ANXIETY
ANXIETY
ANXIETY
ANXIETY
ANXIETY
ANXIETY
ANXIETY













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.